Astronomers at the Max Planck Institute for Astronomy just build a detail , three - dimensional map of the cosmic dust in our galaxy .
The map makes economic consumption of 130 million spectrum from the European Space Agency ’s Gaia mission to reveal properties of the dust , which haze over the cosmos between our earth and just about everything else in the Milky Way . The 3D single-valued function indicate where the cloud most muddies the urine of the universe , as well as charts the realm where the “ extinction ” of light is less affected by the particulate affair . The squad ’s research waspublishedtoday in Science .
The dust wring our aspect of whizz and other consistency , making them appear red and fainter than they really are . The latter effect is also known as extinction , or the absorption and sprinkling of setting twinkle by intermediate object — in this case , dust grains .

An artist’s impression of the Milky Way, seen edge-on.Image: ESA/Gaia/DPAC, Stefan Payne-Wardenaar
Of the 220 million spectrum released by the Gaia mission in June 2022 , the research team selected 130 million stars that they determined would be utilitarian for their debris search .
The researchers then trained a neuronic web — a political machine erudition system that draws conclusion by mimicking the summons of neurons in a genius — to render spectrum based on the properties of the small grouping of stars , along with the properties of the dust itself .
The visualization above shows how the extinction curve cause by dust manifests itself around our Sun , up to 8,000 light - years in every counselling . carmine region in the graphical show where the extinction of light is more dependent on the wavelength of the light , whereas extermination is not so dependent on wavelength in blue regions .
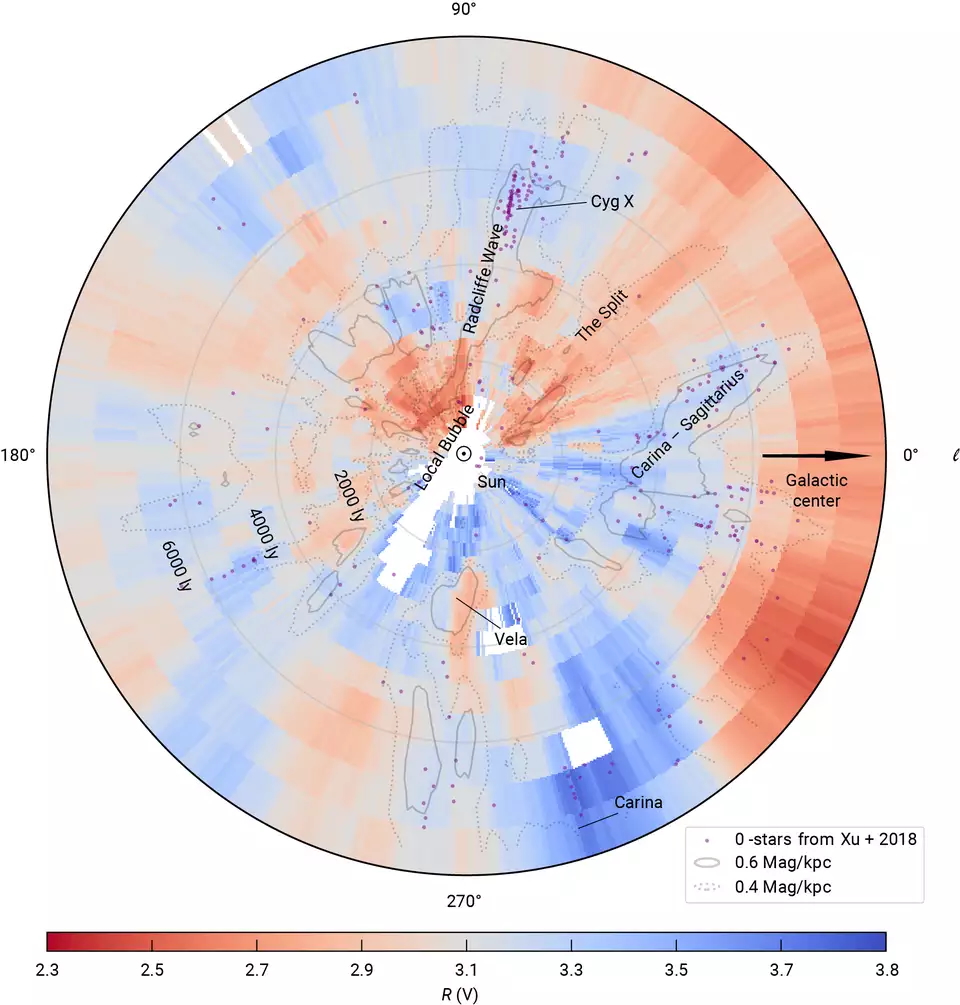
A visualization of the extinction curve of light caused by the dust, out to 8,000 light-years from the Sun. Graphic: X. Zhang/G. Green, MPIA
Grey contouring shows areas of higher detritus density in the map . And if the graphic above make you lose sight of the grandeur covered in this part of the universe , just look at the Webb Space Telescope’sarresting shotof the Carina Nebula ( at the bottom of the above image ) .
fit in to a Max Planck Instituterelease , the 3D map also uncover that the extinction breaking ball for denser region of dust ( corresponding to a little over 20 pounds , or 10 kilo , of rubble in a sphere with Earth ’s wheel spoke ) was steep than expected . The researchers suspect the outrageous curve ball may be get by an abundant form of hydrocarbon in the cosmea — a position they hope to sympathize with more observations .
Gaia collectedmore than three trillion observationsof the milklike Way between July 24 , 2014 and January 15 , 2025 , after which the intrepid spacecraft right away sack out . Gaia ’s datum helped scientist produce the best reconstructed view of our galaxy as it would appear to an outside perceiver in January , but function is not all it did : The scope also has a great cartroad track record with smuggled holes , helping researchers identify theheaviest star - mass black holein April 2024 and spotting theclosest - known black holeto Earth in 2022 .

AstronomycosmosDustmapsStellar astronomy
Daily Newsletter
Get the best technical school , science , and polish news show in your inbox daily .
intelligence from the future , pitch to your present tense .
You May Also Like














