When you buy through links on our internet site , we may take in an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it works .
Imagine a thunderstorm so massive that its sullen schema wrap around the entire major planet .
Such terrific " megastorms " are common onSaturn . Also called " Great White Spots , " they recrudesce once every 20 or 30 years in the planet ’s northern cerebral hemisphere and rage nonstop for months . Astronomers have spotted six of these planet - wide violent storm lash around on Saturn since 1876 . The mostrecent storm struck in December 2010 , whenNASA ’s Cassini space vehicle happened to be orbiting the major planet , snag a front - dustup horizon of the megastorm ’s full 200 - 24-hour interval life span .

A closeup of the 2010 megastorm that formed in Saturn’s northern hemisphere, wrapping around the entire planet
Now , unexampled research into the epical 2010 storm has found that those 200 days of thunder were just a few drops in a much large , uncanny meteorological bucket . According to recent radio scope scans , the ongoing impact of megastorms that erupted on Saturn more than 100 year ago are still visible in the satellite ’s atmospheric state today , and they get out behind persistent chemical substance anomalies that scientist ca n’t amply explain .
In other word , long after a megastorm disappearance from eyeshot , its wallop on Saturn ’s atmospheric condition hold up centuries .
" For most of the fourth dimension , Saturn ’s atmosphere attend brumous and featureless to the defenseless eye in contrast toJupiter ’s coloured and vivacious atmosphere , " the researcher write in a study published Aug. 11 in the journalScience advance . " This movie change when we look at Saturn using a radio eye . "
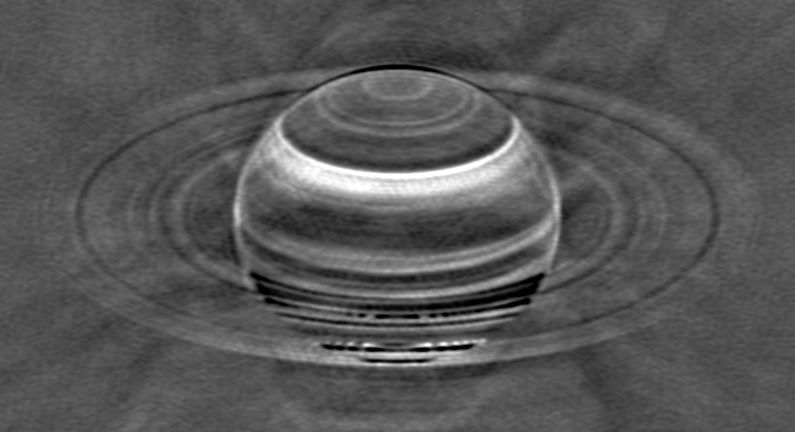
Radio image of Saturn taken with the VLA in May 2015, with the brighter radio emissions from Saturn and its rings subtracted. Since ammonia blocks radio waves, the bright features indicate areas where ammonia is depleted and the VLA could see deeper in the atmosphere.
Related : Strange radio signal detected from Earth - like planet could be a magnetic field necessary for life
Using the Very Large Array radio telescope in New Mexico , the study authors peered through the haze of Saturn ’s upper atmosphere , hoping to discover chemical substance leftover of the vast 2010 megastorm . In fact , the team find traces of all six recorded megastorms , the earliest of which hit more than 130 years ago , as well as a potentially unexampled tempest never recorded before .
seeable only inradio wavelength , those remnants took the form of largeammonia gasanomalies . Saturn ’s uppermost cloud stratum is made mainly of ammonia - ice cloud . But in their radio reflexion , the researcher project regions of unexpectedly low ammonia compactness just below this cloud layer in area associated with past storm . Meanwhile , century of mile below these same atmospherical regions , ammonia concentration spiked much higher than normal .

— 6 reason astrobiologists are holding out hope for life on Mars
— The 7 strangest asteroid : uncanny space rocks in our solar system
— Voyager to Mars rover : NASA ’s 10 greatest innovations

The implication , accord to the study authors , is that megastorms seem to drive some mysterious ammonia transport process that draw ammonia gas from Saturn ’s upper atmosphere into the depths of the depleted standard atmosphere — peradventure in the form of a " mushball " rain in which icy hail balls of ammonia fall through the atmosphere before reevaporating again . This drippy process come along to last hundreds of years after a tempest visibly vanishes , the research worker wrote .
While the mechanism behind these atmospheric anomaly — and behind Saturn ’s megastorms in general — remain a mystery , studying them further could broaden not only our savvy of how jumbo planets var. but also of what drive storm systems like Saturn ’s Great White Spots and Jupiter ’s even largerGreat Red Spotto develop so inexplicably large , accord to the researchers .
" understand the mechanisms of the largest violent storm in thesolar systemputs the possibility of hurricane into a wide cosmic circumstance , challenging our current noesis and tug the boundary of sublunary weather forecasting , " trail written report authorCheng Li , formerly at the University of California , Berkeley and now an adjunct prof at the University of Michigan , said in astatement .















